In the rapidly evolving energy landscape, the selection of the right power transformer has become increasingly critical for both industrial applications and residential needs. As noted by leading industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a senior engineer at the Global Energy Solutions Institute, "The right power transformer not only ensures the efficiency of power distribution but also significantly impacts the overall sustainability of electrical systems." The importance of making an informed choice cannot be overstated, especially with the diverse range of transformers available on the market today.
Choosing the appropriate power transformer involves a comprehensive understanding of one's specific requirements, including voltage levels, load capacity, and environmental considerations. Each decision impacts not just performance but also long-term operational costs and energy efficiency. As power demands continue to rise, aligning the needs of the modern user with the technical specifications of power transformers is essential for optimizing energy use and minimizing environmental footprints. By delving into the key factors influencing transformer selection, this guide aims to equip readers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of power transformer acquisition effectively.

When selecting a power transformer, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles of how these devices operate.
A power transformer is a critical component in electrical systems, designed to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. This process involves alternating current to create a magnetic field in the transformer's core, allowing it to step up or step down voltage levels according to user requirements. Understanding these basics helps in identifying the right type of transformer for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Moreover, the functionality of a power transformer extends beyond mere voltage conversion. Transformers play a key role in managing power distribution, improving voltage stability, and reducing transmission losses.
Factors such as efficiency rating, load capacity, and cooling mechanisms need to be considered when assessing potential transformers. By grasping the basics of transformer operation and their functional capabilities, users can make informed decisions, ultimately selecting the right transformer that aligns with their energy demands and operational needs.
When selecting a power transformer, understanding the various types available is crucial in ensuring you choose the best fit for your specific applications. Power transformers can be broadly classified into several categories, including step-up and step-down transformers, isolation transformers, and auto transformers. Step-up transformers increase voltage from the primary to secondary winding, making them ideal for applications that require high voltage transmission over long distances. Conversely, step-down transformers are designed to reduce voltage levels, essential for providing usable power in residential or commercial settings.
Another important type is the isolation transformer, which serves to isolate electrical devices from the power source, thereby enhancing safety and protecting sensitive equipment from voltage spikes. These transformers are particularly useful in industrial environments where equipment needs protection from electrical noise and interference. Lastly, auto transformers utilize a single winding for both primary and secondary circuits, making them more compact and cost-effective for certain applications, although they do not provide electrical isolation. Understanding the functionalities and best-use scenarios for these various transformer types will aid in making an informed decision that aligns with your energy needs.
When selecting a power transformer, it's crucial to consider several key factors that will ensure optimal performance and longevity. First and foremost, understanding the power rating is essential. According to industry reports from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), selecting a transformer with appropriate voltage levels and capacity can significantly impact efficiency. A transformer’s capacity should typically exceed the maximum expected load by at least 20% to ensure reliability without risking overheating or failure.
Another critical aspect is the application environment. Transformers designed for industrial use may require protective features against environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. A study by the Electric Power Research Institute highlighted that the right choice of insulation materials and housing can extend a transformer's life by 30% in harsh conditions. Therefore, assessing the installation location and conditions can lead to better operational sustainability.
Tips: Always consult with a certified engineer who specializes in electrical systems to review specifications before making a purchase. This can help identify potential issues early on. Additionally, compare efficiency ratings, as a higher initial investment in a more efficient transformer can lead to lower operating costs over time.
| Factors | Description | Importance Level | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Rating | Determine the wattage needed to support your loads. | High | Choose a transformer with a rating exceeding your maximum anticipated load. |
| Voltage Requirements | Specify primary and secondary voltage levels. | High | Ensure compatibility with your existing electrical system. |
| Efficiency | Assess the efficiency rating to minimize energy loss. | Medium | Higher efficiency models may have a higher upfront cost but save on energy bills. |
| Cooling Type | Choose between air-cooled and oil-cooled transformers. | Medium | Oil-cooled transformers tend to have higher power ratings. |
| Size and Weight | Consider the physical dimensions and weight for installation. | Low | Ensure space availability and support for heavy units. |
| Regulatory Standards | Confirm compliance with local and international electrical codes. | High | Non-compliance can lead to safety hazards or legal issues. |
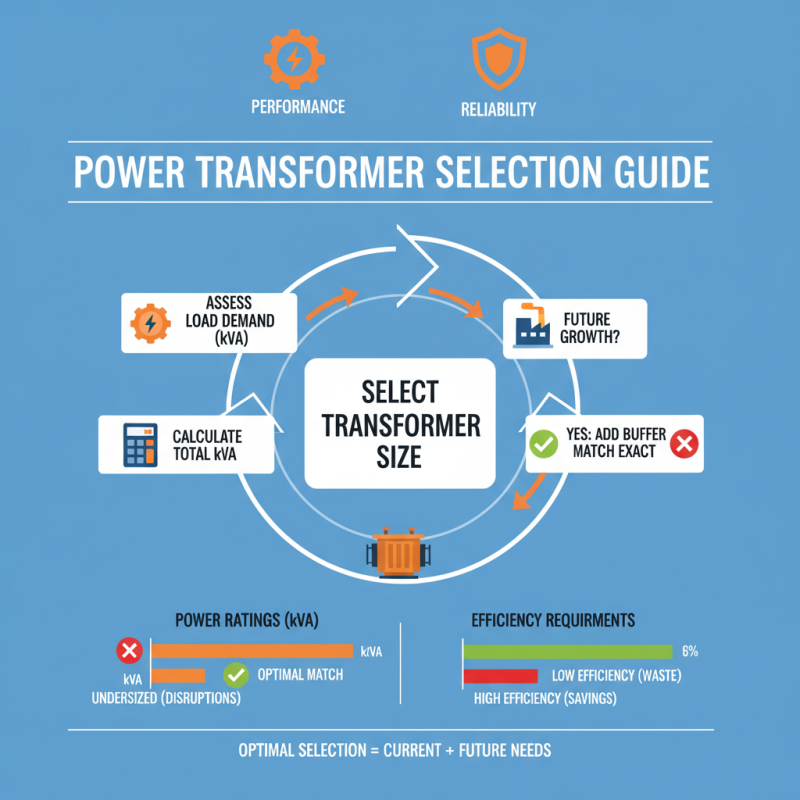
When selecting a power transformer, understanding power ratings and efficiency requirements is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in your application. Power ratings indicate the maximum load that a transformer can handle, expressed in kilovolt-amperes (kVA). It is essential to evaluate the total load demand of your system to determine the appropriate transformer size. Overloading a transformer can lead to overheating and eventual failure, while an undersized transformer may not meet operational needs, causing disruptions. Therefore, a clear assessment of both current and future load requirements is necessary for effective transformer selection.
Efficiency is another vital factor to consider when choosing a power transformer. Transformers operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, and as such, some energy is inevitably lost in the process, primarily as heat. The efficiency rating, which is usually expressed as a percentage, reflects how much of the input electrical power is converted to output power. Higher efficiency transformers can lead to significant energy savings and lower operational costs over time. It is also important to analyze energy efficiency standards and regulations applicable in your region to ensure compliance while maximizing the benefits of your investment. Selecting a transformer with optimal efficiency, tailored to your specific power requirements, will enhance your system's overall performance and sustainability.
When it comes to the installation and maintenance of power transformers, careful consideration is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. According to industry reports, improper installation can lead to a 30% increase in operational costs, emphasizing the importance of adhering to standardized installation practices. Key installation factors include ensuring proper site selection, environmental conditions, and anchor arrangements to prevent transformer movement and to allow adequate cooling.
Additionally, specific guidelines outlined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) recommend maintaining a safe distance from structures and vegetation to mitigate the risk of fire hazards.
On maintenance, the IEEE also highlights that regular inspections can significantly extend a transformer's life span. Routine checks should include monitoring insulation resistance, checking for signs of overheating, and evaluating fluid levels. The 2023 Transformer Maintenance Report indicates that facilities with proactive maintenance schedules can reduce failure rates by up to 40%, ultimately leading to lower repair costs and enhanced reliability. Implementing a predictive maintenance strategy, such as utilizing thermal imaging and condition monitoring technologies, allows operators to anticipate potential issues before they escalate into costly outages.
By focusing on both proper installation and diligent maintenance, users can ensure their transformers operate efficiently and safely over their intended service life.