In today's rapidly evolving energy landscape, the selection of large electrical transformers is a critical decision for utilities, industrial facilities, and commercial operations alike. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the demand for reliable and efficient power management solutions is expected to rise by over 30% in the next decade, driven by the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the electrification of transportation systems. As a cornerstone of electrical infrastructure, large electrical transformers play a vital role in voltage regulation and power distribution, posing a unique challenge for decision-makers tasked with ensuring operational efficiency and compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
The global market for large electrical transformers was valued at approximately $10 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow significantly, reaching nearly $16 billion by 2030, as reported by MarketsandMarkets. This growth underscores the need for carefully considering the specifications and operational requirements when selecting transformers, including capacity, configuration, and cooling methods. With the urgency of energy transition and increased investment in grid modernization, understanding the intricacies of large electrical transformers is essential for optimizing performance while minimizing total cost of ownership and enhancing grid stability. As we explore the process of choosing the right large electrical transformers, we will provide insights into key factors and best practices that can guide decision-making in this complex field.

Large electrical transformers play a crucial role in the efficient distribution of electrical power in various industries. Understanding their basic components and functions is essential for making informed decisions when selecting the right transformer for specific needs. Transformers primarily consist of three key parts: the core, the windings, and the tank. The core, usually made from silicon steel, facilitates the magnetic flux necessary for energy transfer, while the windings—composed of copper or aluminum—are responsible for conducting electricity.
According to a recent report from the Global Market Insights, the demand for large transformers is projected to reach over $29 billion by 2026, driven by the increasing investments in the renewable energy sector and smart grid technologies. These advancements necessitate transformers that can handle higher voltage levels and offer improved energy efficiency. Additionally, the installation of large electrical transformers must consider factors like load capacity, operational environment, and regulatory compliance to ensure optimal functionality and longevity. With these considerations in mind, stakeholders can better navigate their options in the transformer market.
| Transformer Type | Power Rating (kVA) | Voltage Level (kV) | Cooling Method | Weight (kg) | Dimensions (mm) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil-Immersed Transformer | 1500 | 10 | ONAN | 1200 | 2000 x 1000 x 1800 | 98.5 |
| Dry-Type Transformer | 1000 | 6.6 | Natural Air-Cooled | 800 | 1500 x 800 x 1200 | 97.5 |
| Specialty Transformer | 500 | 12 | Forced Air-Cooled | 600 | 1800 x 900 x 1500 | 96.0 |
When selecting the right large electrical transformers, identifying your power requirements and load needs is crucial. Start by assessing the total power consumption of all appliances and machinery that will be running simultaneously. This involves calculating the combined wattage of all devices, accounting for both continuous and peak loads. Understanding the voltage requirements of your systems also plays a significant role, as transformers must be compatible with the input and output voltage levels to function efficiently.
Next, consider the type of loads your transformer will support. Different applications may require transformers with specific characteristics, such as isolated or ungrounded systems for sensitive equipment, or specific frequency ratings for specialized machinery. Additionally, take into account future expansion or changes in load demands; selecting a transformer with some extra capacity can help accommodate unexpected increases in power requirements. By thoroughly evaluating these parameters, you can choose a transformer that not only meets current needs but also provides flexibility for future growth.
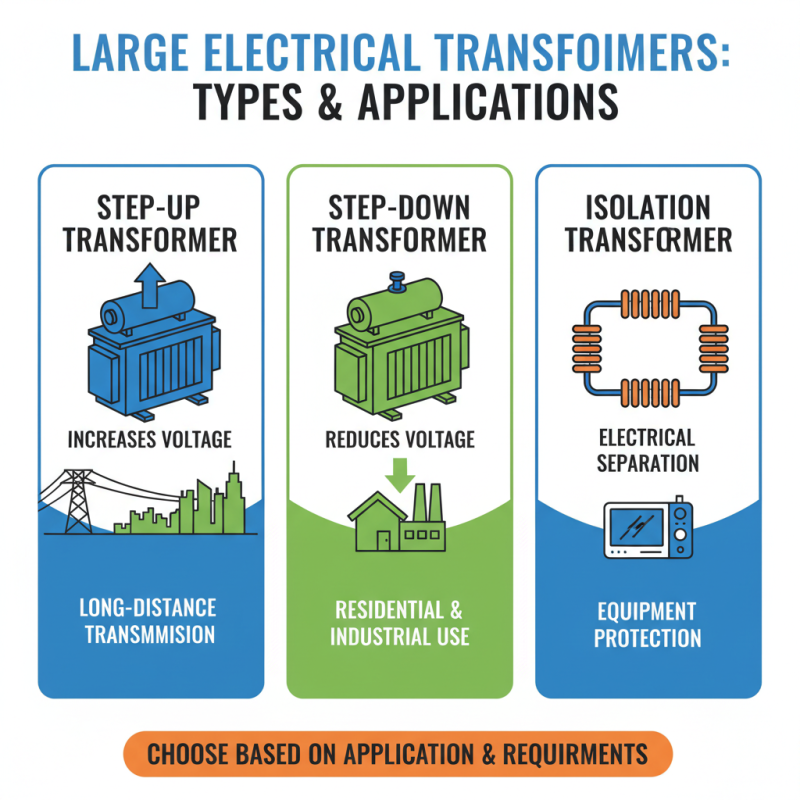
When evaluating different types of large electrical transformers, it is essential to consider the specific applications and requirements they will serve. Large transformers typically fall into various categories, including step-up, step-down, and isolation transformers. Step-up transformers increase voltage levels, making them ideal for applications that require high-voltage transmission over long distances. Conversely, step-down transformers reduce voltage levels, suitable for powering residential or industrial equipment that operates at lower voltages.
Another critical factor in the evaluation process is understanding the cooling methods employed by the transformers. Large transformers often use either air-cooling or oil-cooling systems. Oil-cooled transformers are generally preferred for their efficiency and capability to manage higher loads, while air-cooled transformers are advantageous in areas where space is restricted. Additionally, evaluating factors such as load capacity, impedance, and maintenance requirements will help ensure that the right transformer is chosen to meet operational demands and efficiency goals.
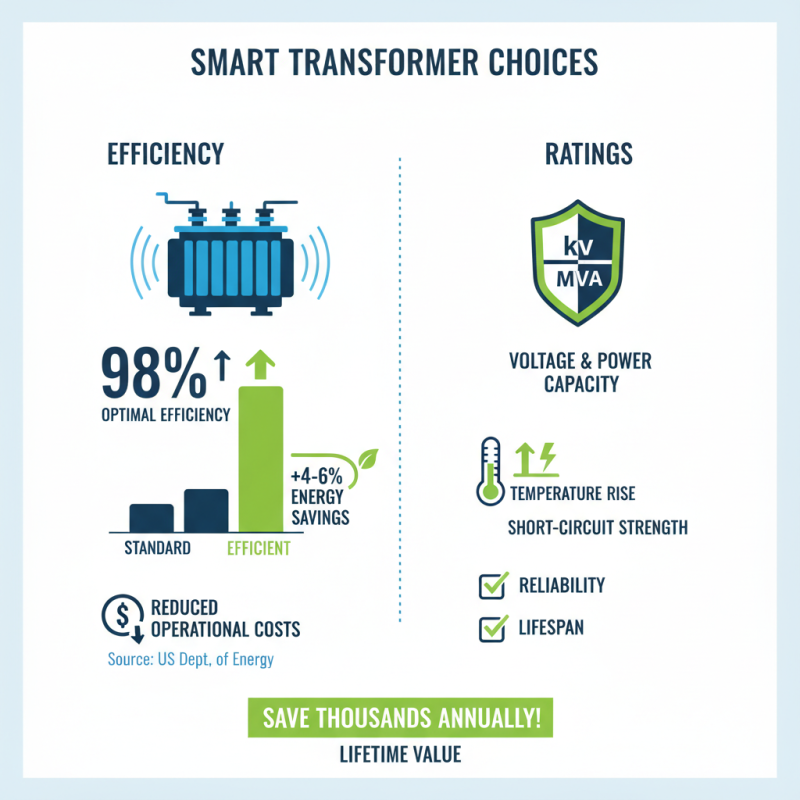
When choosing large electrical transformers, efficiency and ratings are critical considerations that can significantly impact operational costs and performance. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, improvements in transformer efficiency can lead to energy savings of 4-6% over standard designs, translating into substantial reductions in lifetime energy costs. For example, a well-designed transformer operating at 98% efficiency can save an organization thousands of dollars annually in energy expenses compared to a less efficient model.
Moreover, understanding the different ratings is essential to ensure that a transformer meets your specific application needs. The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) provides comprehensive guidelines on transformer ratings, including KVA rating, voltage levels, and impedance. It’s important to select a transformer that not only matches the load requirements but also operates efficiently under varying electrical loads. Selecting the right efficiency class, as per NEMA Premium standards, can enhance reliability and reduce losses, with premium efficiency transformers often offering efficiencies of 97% or higher. This careful evaluation of efficiency and ratings helps in maximizing both performance and cost-effectiveness in the long run.
When selecting large electrical transformers, understanding installation and maintenance needs is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Firstly, consider the installation environment, which includes factors such as space, accessibility, and grounding requirements.
Transformers require adequate ventilation and must be positioned to facilitate easy access for maintenance and inspections. Evaluating the site for potential hazards, including moisture or extreme temperatures, can significantly impact the transformer’s operational efficiency and lifespan.
Maintenance needs are also paramount in ensuring the reliability of large transformers. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear, overheating, and leaks. It is essential to establish a proactive maintenance schedule that includes cleaning, testing insulation resistance, and monitoring fluid levels. Additionally, ensuring that the staff responsible for maintenance are well-trained and familiar with the specific transformer model will help in identifying potential issues before they escalate. Planning for proper maintenance not only enhances transformer performance but also minimizes downtime and repair costs.