A dry transformer is an essential component in various electrical systems, providing voltage transformation without the use of liquid insulation. Unlike traditional transformers that utilize oil for cooling and insulation, dry transformers rely on air or solid insulating materials to perform these functions. This innovative design makes dry transformers an increasingly popular choice for numerous applications, particularly in environments where safety, maintenance, and environmental considerations are paramount.
The operation of a dry transformer involves the conversion of electrical energy from one voltage level to another, allowing for efficient power distribution across different sectors. Its construction typically features a core made of high-quality magnetic materials, which enhances energy efficiency and reduces losses during the transformation process. With their robust design and versatility, dry transformers are widely employed in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and renewable energy installations, contributing to the reliability and effectiveness of electrical systems globally.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the workings of dry transformers, exploring their advantages, applications, and the key principles that underpin their functionality. Understanding the mechanics and benefits of dry transformers is crucial for professionals in the electrical field, as well as for those interested in sustainable and innovative energy solutions.
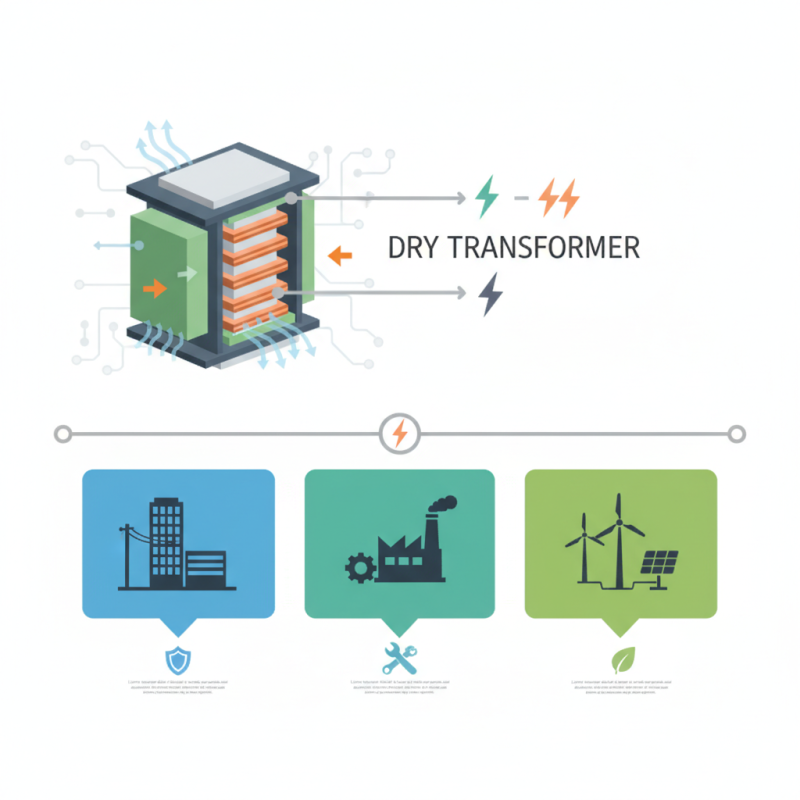
A dry transformer is a crucial component in electrical systems, designed to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction without the use of liquid insulating materials. This type of transformer relies on air or solid insulation, which significantly reduces the risk of environmental contamination and makes it suitable for indoor applications. Dry transformers come in various configurations, including single-phase and three-phase types, and are widely used in commercial and industrial settings for stepping up or down voltage levels.
The operation of a dry transformer involves passed alternating current (AC) through its primary winding, generating a magnetic field. This magnetic field then induces a voltage in the secondary winding, according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. One of the key advantages of dry transformers is their ability to provide a reliable and efficient means of voltage transformation while maintaining a lower risk of fire hazards. Additionally, their compact design allows for flexibility in installation and makes them a preferred choice in areas where space is limited. Overall, dry transformers play a vital role in ensuring the stability and efficiency of electrical distribution systems.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Dry Transformer |
| Cooling Method | Air Cooling |
| Insulation Type | Solid Insulation |
| Application | Indoor Use |
| Voltage Rating | Up to 35 kV |
| Efficiency | 95% - 99% |
| Weight | Lighter than Liquid Transformers |
| Environmental Impact | Lower Risk of Leakage |
A dry transformer is an essential component in electrical systems, designed to efficiently step up or step down voltage levels while minimizing environmental risks. Key components of a dry transformer include the core, windings, insulation, and cooling system. The core, typically made of high-grade silicon steel, serves to channel magnetic flux, ultimately improving the efficiency of the transformer by reducing energy losses.
The windings, composed of insulated copper or aluminum, are crucial for transferring electrical energy. They are positioned around the core and are responsible for creating the electromagnetic field necessary for the transformation of voltage. Proper insulation materials are used to separate these windings, ensuring safety and preventing short circuits. Additionally, dry transformers utilize air or a specialized cooling mechanism to dissipate heat, maintaining optimal operating temperatures and enhancing reliability in various applications.
Together, these components work seamlessly to ensure that the dry transformer operates efficiently within electrical systems while providing a safe environment.
Dry transformers are electrical devices that transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Unlike traditional transformers, they do not use liquid coolants, making them safer and more environmentally friendly.
The principle of operation of dry transformers is based on the transformation of alternating current (AC) from a primary coil to a secondary coil through a magnetic core, typically made of laminated silicon steel. According to industry reports, dry transformers are estimated to have an average efficiency of around 98-99%, which makes them highly effective for various applications.
The working mechanism involves the generation of a magnetic field as current flows through the primary winding. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding, thus enabling power transfer without direct electrical contact. The absence of insulating oil eliminates the risk of leaks and fire hazards, enhancing safety in industrial and commercial applications. Additionally, dry transformers are more suitable for indoor use since they do not emit harmful substances, and their sturdy construction can withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Data from market analysis reveal that dry transformer usage is on the rise by approximately 5% annually, driven by their increasing application in renewable energy systems and energy-efficient buildings.

Dry transformers are increasingly recognized for their efficiency and environmental benefits in various electrical systems. One of the primary applications of dry transformers lies in commercial buildings, such as shopping malls and office complexes, where they provide reliable power distribution while minimizing fire hazards. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), dry transformers can achieve energy losses as low as 0.5%, making them a more sustainable choice compared to traditional oil-filled transformers.
Additionally, dry transformers are often employed in renewable energy sectors, particularly in wind and solar power facilities. Their ability to operate effectively in harsh environmental conditions—such as high humidity or extreme temperatures—makes them suitable for outdoor installations. A study from the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) indicates that the demand for dry transformers in renewable energy applications is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8% over the next five years. This trend underlines the role of dry transformers in supporting the transition towards sustainable energy systems while ensuring enhanced safety and reliability in power distribution.
Dry transformers, as non-liquid insulated devices, offer several advantages and disadvantages that impact their application in electrical systems. One major advantage is their enhanced safety profile. Since they use air as an insulator rather than liquid oil, they eliminate risks associated with fire hazards and environmental contamination. According to a report by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), dry transformers can significantly reduce the chances of harmful leaks, making them an ideal choice for environments like schools and hospitals that prioritize safety.
On the downside, dry transformers tend to be larger and heavier compared to traditional oil-filled transformers, which can complicate installation in space-constrained areas. Additionally, they generally have lower thermal performance, operating at temperatures that can limit their efficiency under heavy loads. A study published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) indicates that while dry transformers typically handle loads up to 500kVA effectively, they may struggle in applications requiring higher capacities without additional cooling measures. Therefore, while dry transformers offer distinct safety benefits, their physical and performance limitations must be carefully considered in system design.