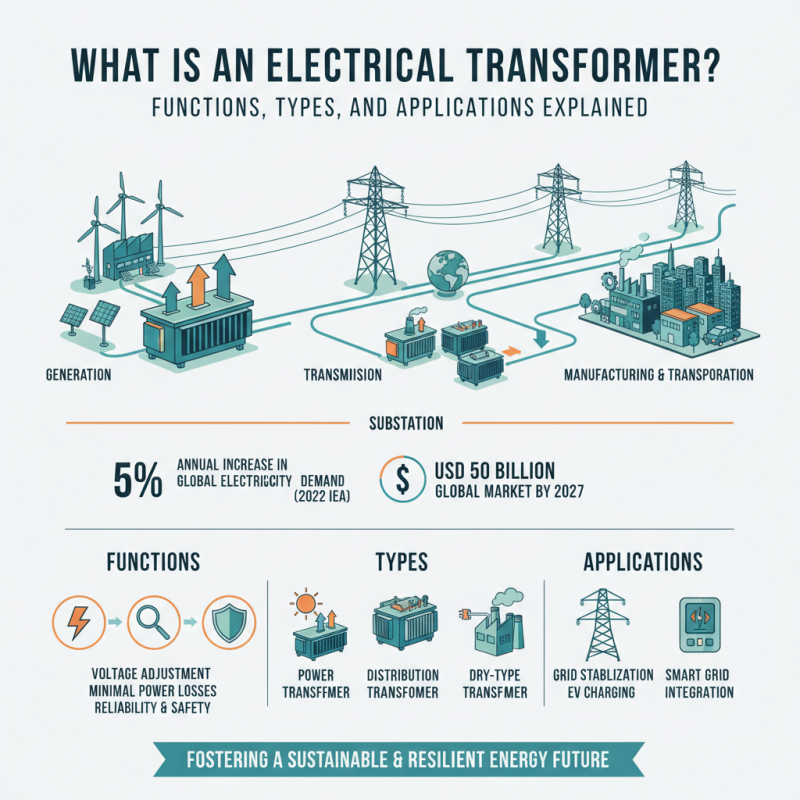
The electrical transformer is a critical component in the modern electrical grid, playing an indispensable role in the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), as of 2022, the global electricity demand is projected to increase by 5% annually, necessitating the efficient management and transformation of voltage levels to ensure reliability and safety in the supply of electricity. With such a significant rise in demand, the importance of electrical transformers cannot be overstated, as they facilitate the adjustment of voltage from generation to consumption levels, ensuring minimal power losses and optimal efficiency.
Furthermore, the global transformer market is anticipated to grow considerably, driven by investments in renewable energy sources and advancements in smart grid technology. Research firm MarketsandMarkets estimates that the electrical transformer market will reach USD 50 billion by 2027, highlighting the increasing reliance on these devices across various sectors such as energy, manufacturing, and transportation. Different types of electrical transformers are employed in myriad applications—from stepping up voltage for transmission lines to stepping down voltage for residential use—underscoring their versatility and vital function in our interconnected electrical systems. As we explore the various functions, types, and applications of electrical transformers, it is essential to recognize their role in fostering a sustainable and resilient energy future.
An electrical transformer is a crucial device in the electrical power distribution system, designed to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. At its core, a transformer converts voltage levels, either boosting or reducing them to ensure efficient power transmission. The basic principle behind a transformer operates on Faraday's Law of electromagnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field in the primary coil induces a voltage in the secondary coil. This design allows for the efficient movement of electricity over long distances, making it fundamental in modern energy systems.
**Tips:** When choosing a transformer, consider factors such as power rating, voltage requirements, and installation environment to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Transformers come in various types, each suited to specific applications. Step-up transformers increase voltage, making them ideal for long-distance power transmission. Conversely, step-down transformers reduce voltage for safe usage in residential and commercial applications. Additionally, specialized transformers, like isolation transformers, provide safety and stability in sensitive electronic devices. By understanding these basic principles and functions, you can appreciate how transformers play a vital role in the global energy landscape.
**Tips:** Regular maintenance and monitoring of transformers are essential. This ensures reliability and prevents potential failures that can lead to significant downtime and repair costs.
Electrical transformers play a critical role in power distribution systems, primarily by facilitating the efficient transmission of electrical energy over long distances. One of the key functions of transformers is voltage transformation, which adjusts the voltage levels to minimize energy losses during transmission. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), a well-designed power distribution system can reduce energy losses to less than 10%, significantly optimizing overall system efficiency. By stepping up voltage for transmission and stepping it down for end-use, transformers enable a stable and reliable electricity supply to residential, commercial, and industrial consumers.
Another essential function of transformers is isolation, which helps in protecting equipment and enhancing safety. Isolation transformers reduce the transfer of electrical noise and disturbances from the power supply to sensitive equipment, thus improving the reliability of power systems. The Energy Information Administration (EIA) highlights that deploying isolation transformers contributes to the longevity of both distribution infrastructure and consumer appliances. Furthermore, transformers support the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid, allowing for better management of variable power flows and ensuring that power quality remains high, even with fluctuating supply from solar and wind energy resources.
Electrical transformers are essential devices that efficiently transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. They are categorized into various types, each designed for specific applications. Common types include step-up and step-down transformers, which alter voltage levels to meet the needs of different electrical systems. Isolating transformers provide galvanic isolation, while autotransformers offer a more compact design for voltage adjustment. Each type plays a pivotal role in power distribution, ensuring that electricity is delivered safely and effectively across long distances.
When selecting a transformer, it is essential to consider its application to ensure optimal performance. For instance, industrial settings often require heavy-duty transformers to handle high loads, while residential areas might utilize smaller, more efficient units. Tips for maintaining transformer efficiency include regular inspections and timely upgrades to accommodate changing load requirements. Understanding the specific functions and applications of different transformer types can significantly enhance energy management and reliability within electrical systems.

The efficiency of electrical transformers plays a crucial role in determining energy losses during transmission. A transformer's efficiency is typically expressed as the ratio of the output power to the input power, reflecting how effectively it converts electrical energy from one voltage level to another. High-efficiency transformers minimize energy loss, primarily due to heat generated from resistive losses in windings and core losses due to magnetic hysteresis and eddy currents. As efficiency increases, the amount of energy lost as waste heat decreases, resulting in better performance metrics and lower operational costs for power systems.
Moreover, the impact of transformer efficiency extends beyond just energy conservation. High-efficiency transformers lead to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint when deployed in large-scale power distribution systems. Energy losses not only represent a substantial economic cost but, when aggregated across an electrical grid, can lead to significant environmental repercussions. Therefore, the design and selection of transformers with optimal efficiency become essential, especially in modern applications where sustainability and reliability are paramount. Addressing these efficiency concerns contributes to the overall robustness of electrical networks and their ability to meet growing energy demands.
The future of transformer technology is being significantly shaped by the integration of smart grid systems and renewable energy sources. As the demand for efficient energy solutions grows, transformers are evolving to accommodate the fluctuating supply and demand characteristic of renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Smart grids enable real-time monitoring and control of electrical networks, which helps transformers to optimize energy distribution, reduce losses, and enhance overall grid reliability. By incorporating data analytics and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, transformers can adjust their operations dynamically, ensuring that energy distribution adapts to changing conditions.
In addition to improving efficiency, the integration of transformers within smart grid frameworks facilitates greater use of renewable energy. Modern transformers are now being designed to handle the variability of sources such as solar panels and wind turbines. These transformers not only step up or step down voltage levels but are also equipped with advanced functionalities like voltage regulation and fault detection. As utilities aim to minimize carbon footprints and maximize renewable resource utilization, transformers that can seamlessly interface with smart grids become crucial in supporting sustainable energy goals and driving the transition to cleaner energy systems.