In the field of power transformer testing, achieving optimal standards is crucial. Understanding the nuances of this process can make a significant difference. Power transformers play a vital role in power distribution systems. Ensuring their reliability through comprehensive testing is non-negotiable.
Testing power transformers requires attention to detail. Proper planning and execution can prevent costly failures. Many overlook the importance of a thorough testing strategy. Frequent mistakes in testing procedures can lead to inaccurate results. Each test must be tailored to the specific transformer model being evaluated.
The task is not straightforward. Environments can vary significantly. This variability may affect test outcomes. Empowering technicians with the right knowledge is essential for success in power transformer testing. Aspects like temperature, humidity, and equipment condition deserve careful consideration. Regular reviews and adaptations can enhance the testing process. Emphasizing continuous learning can help refine strategies.
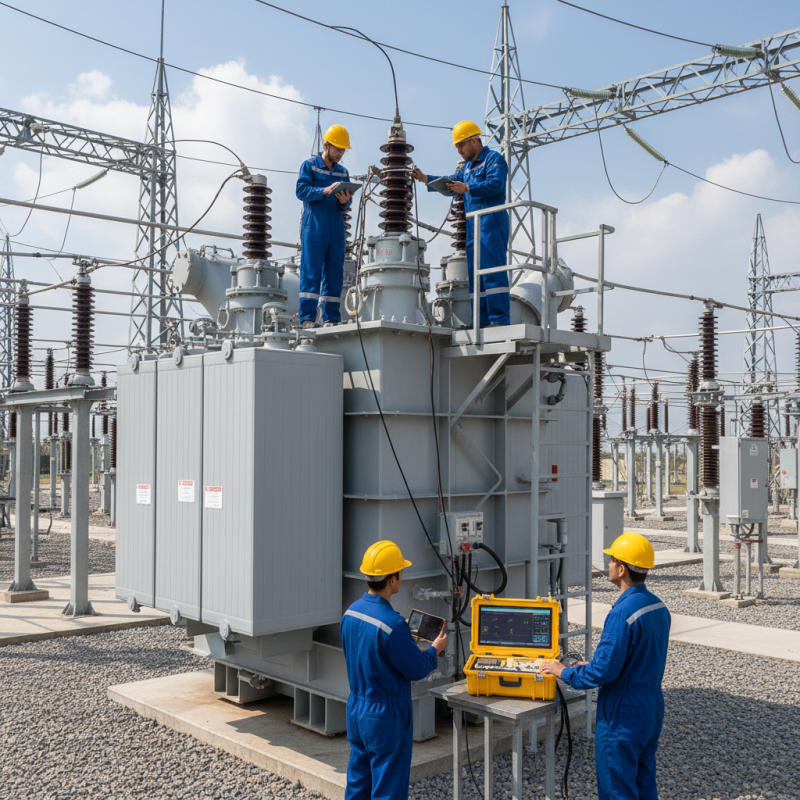

Power transformers are crucial in electrical systems. They step up or step down voltage levels, ensuring efficient power transmission. Understanding their basic functions helps in diagnosing issues effectively. For instance, a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission shows that poorly maintained transformers can lead to energy losses of up to 5-10%.
Regular testing is essential for optimal performance. Insulation resistance testing helps identify potential failures before they escalate. Surprisingly, many operators neglect this step, risking significant downtime. According to IEEE statistics, the average age of transformers in service is over 30 years. Aging components often require more attention and scrutiny.
Another report highlights that transformer failures can cost utilities millions in repair and outage expenses. Even minor anomalies can lead to a complete breakdown. Visual inspections should complement technical testing to detect physical damages. However, many personnel often overlook this critical aspect under the pressure of tight schedules. Empowering teams with knowledge about testing can greatly reduce risks.
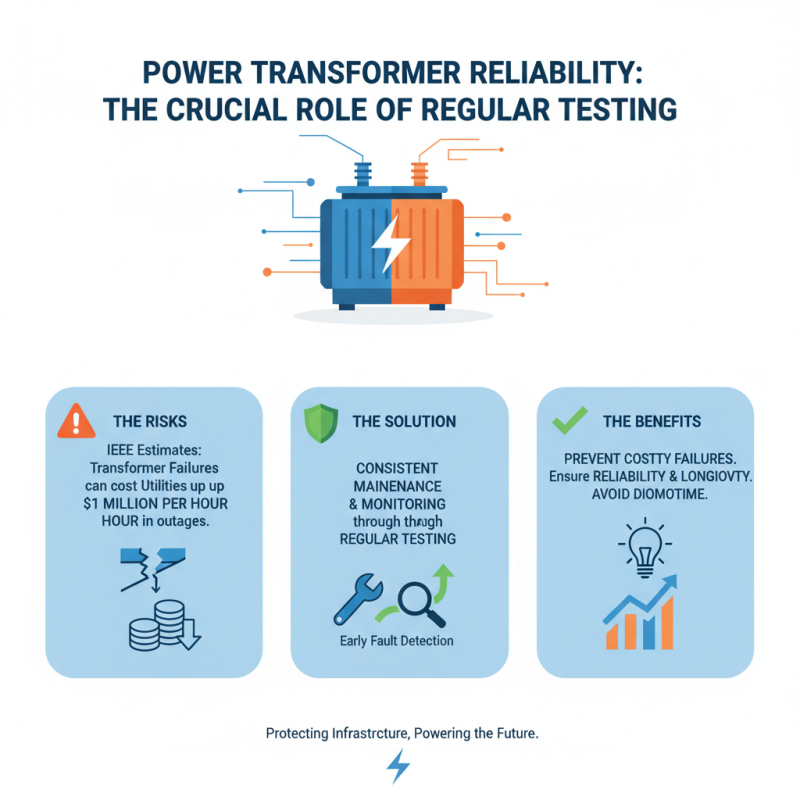
Regular testing of power transformers is crucial for ensuring their reliability and longevity. The IEEE estimates that transformer failures can lead to outages costing utilities up to $1 million per hour. This staggering number underlines the need for consistent maintenance and monitoring. Testing helps identify issues before they escalate, potentially avoiding these expensive failures.
Data from industry reports indicate that approximately 70% of transformer failures stem from insulation breakdown due to aging or moisture contamination. Testing can reveal insulation problems early on. It's vital to conduct tests like Power Factor, Sweep Frequency Response Analysis, and Doble Testing. These check different parameters, shedding light on the transformer's health.
Ignoring regular tests can lead to devastating consequences. Even a minor fault, if unnoticed, can cause extensive damage over time. Yet, some facilities still postpone testing due to budget constraints or scheduling issues. Regular testing is not just an expense; it’s an investment in reliability, safety, and operational efficiency. Routine diagnostics create a safety net, catching issues that could result in costly repairs or replacements later.
Testing power transformers is crucial for ensuring their reliability and efficiency. One key method is insulation resistance testing. This checks the integrity of the insulation materials. A low resistance value may indicate potential failures. It’s important to perform this test in dry conditions, as moisture can affect results.
Another vital method is power factor testing. This evaluates the dielectrics of transformer insulation. It helps identify deterioration over time. Regular testing should be done to track trends and catch issues early. Note that variations in temperature can also impact this test.
Thermal imaging can be insightful as well. It detects hot spots that signal possible failures. Overheating can lead to unexpected shutdowns. Monitoring these areas allows for proactive maintenance. However, results may vary depending on equipment calibration and environmental conditions. Consistency in testing practices is essential for accurate assessments.
| Tip Number | Testing Method | Description | Frequency of Testing | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Insulation Resistance Testing | Measures the resistance of insulation to ensure effective performance. | Annual | Temperature affects readings; ensure proper voltage levels. |
| 2 | Transformer Sweep Frequency Response | Identifies changes in core geometry and winding deformation. | Every 5 years | Avoid external vibrations during testing. |
| 3 | Transformer Turns Ratio Testing | Ensures the correct turns ratio between windings. | Every 2 years | Utilize calibrated equipment for accuracy. |
| 4 | Power Factor Testing | Assesses the dielectric losses in insulation materials. | Annually | Temperature and humidity conditions can influence results. |
| 5 | Dissolved Gas Analysis | Detects and quantifies gases dissolved in the oil. | Every 6 months | Trained personnel should handle samples to avoid contamination. |
| 6 | Circuit Breaker Analysis | Evaluates the operation and timing of the circuit breakers. | Annually | Ensure accurate timing equipment is used. |
| 7 | Frequency Response Analysis | Assesses the state of transformer windings. | Every 3 years | Use real-time data to ensure accuracy. |
| 8 | Temperature Measurement | Monitors the temperature of transformer components. | Continuous | Ensure adequate cooling systems are operational. |
| 9 | Partial Discharge Testing | Detects non-visible discharge within insulation. | Every year | Use advanced sensors for precise detection. |
| 10 | Visual Inspection | Identifies any visible signs of damage or wear. | Quarterly | Look for signs of oil leaks or corrosion. |

Testing power transformers can be risky. Safety precautions are crucial. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes helmets, gloves, and insulated footwear. Keep your workspace clear of clutter. A clean area minimizes accidents and distractions.
Understand your environment. High-voltage zones require extra caution. Use barriers to keep unauthorized personnel away. Ensure all tools are insulated and in good condition. Inspect them regularly for wear and damage. It’s easy to overlook this step, but doing so can prevent serious injuries.
Stay alert during testing. Fatigue can lead to mistakes. Take regular breaks to maintain focus. Communicate clearly with your team. Misunderstandings can create dangerous situations. Never skip safety drills; they prepare everyone for emergencies. Reflect on past experiences. Each test is a learning opportunity.
Understanding the test results of power transformers is crucial for effective maintenance. It can seem overwhelming at first, but clarity comes with practice. Focus on key parameters such as insulation resistance, power factor, and winding resistance. Each result tells a story about the transformer's health. An abnormal reading could indicate potential failures, and immediate action may be necessary.
Regular testing is the foundation of good maintenance practices. Tip: Document all test results over time. This builds a history and helps identify patterns. A sudden change can signal a problem. Relying on a single test is risky, as environmental factors might skew results.
Another point to consider: involve your team in interpreting results. Different perspectives can shed light on potential issues. A fresh set of eyes might catch something overlooked. Collaborate during testing sessions and discuss results openly. This fosters a deeper understanding of the transformer's condition and drives successful maintenance strategies.