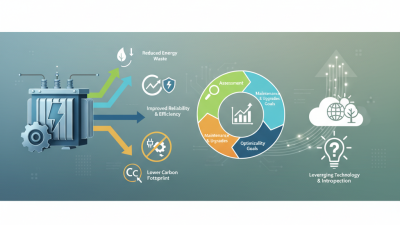
In the evolving landscape of energy demands, understanding the energy efficiency of transformers is crucial. Transformers are key components in electrical distribution systems. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), transformers account for nearly 5% of the global electricity consumption. Improving their efficiency could yield significant energy savings.
By 2026, advancements in technology and regulations may shape the energy efficiency of transformers. The latest standards focus on minimizing losses. This shift aligns with targets set under the Paris Agreement. However, challenges remain in retrofitting existing systems. Not all transformers can meet new efficiency benchmarks.
Evaluating energy efficiency involves benchmarks and metrics. The U.S. Department of Energy has published guidelines indicating efficiency levels for different classes of transformers. Many still operate below optimal levels. The urgency remains to enhance their performance, yet the path forward is intricate. Addressing these complexities is essential for achieving better energy outcomes.

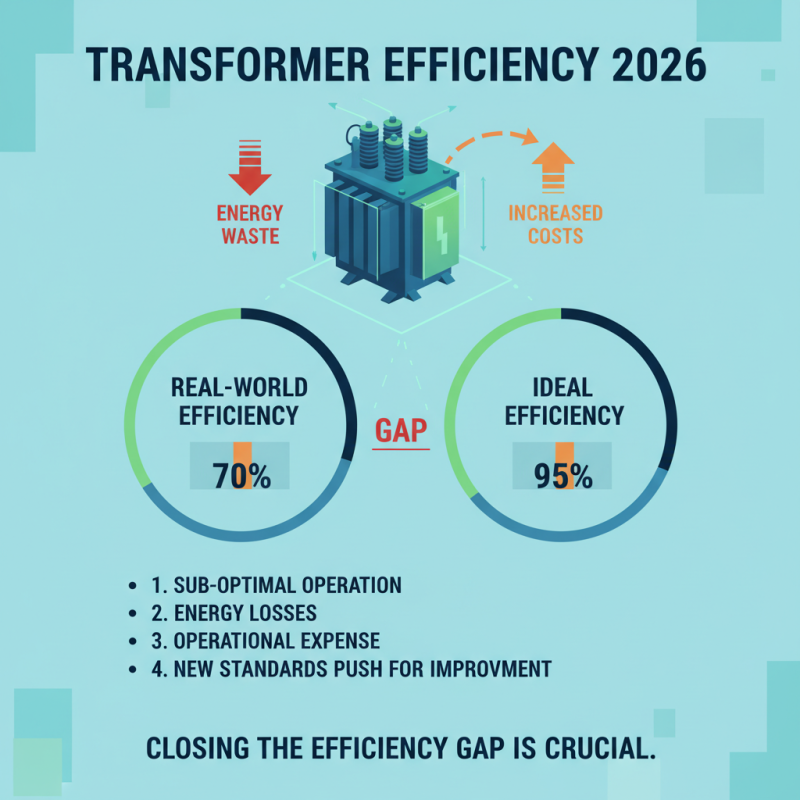
In 2026, transformer energy efficiency remains a significant concern. Many transformers operate at less than optimal efficiency levels. This inefficiency contributes to energy waste and increased operational costs. The current standards aim for improved performance, but the gap between ideal and real-world efficiency is still noticeable.
A variety of factors impact transformer efficiency today. Aging infrastructure often leads to higher losses. Poor maintenance practices may exacerbate these losses. Users sometimes overlook small upgrades that can drastically improve performance. The challenge lies in balancing cost and efficiency. Some facilities hesitate to invest in newer technologies, fearing high upfront costs.
As the push for sustainability grows, awareness of these inefficiencies is crucial. Operators need to assess their systems regularly. Small adjustments can lead to significant savings. However, there is still much room for improvement in overall energy efficiency strategies. Stakeholders must consider not only the initial costs but also long-term benefits.
In 2026, energy efficiency for transformers is shaped by regulatory standards. These standards aim to improve performance and reduce waste. They directly influence how transformers are designed and operated. Regulatory bodies set strict guidelines that manufacturers must follow. Compliance is not optional; it's essential for market access.
Tips: Always stay updated on local regulations. Understanding them will guide purchasing decisions. Evaluate the efficiency ratings of transformers before making investments.
Many older transformers do not meet today's standards. This can lead to energy losses and high operational costs. Operators may face penalties for using inefficient models. Thus, it’s crucial to assess the impact of these regulations on equipment choice.
Tips: Consider upgrading to newer models. They might have higher upfront costs but yield savings in the long run. Monitor your system's performance regularly to identify inefficiencies.
As we approach 2026, the focus on energy efficiency in transformers intensifies. Innovative technologies are emerging, promising to enhance performance.
Smart sensors are one such advancement. They monitor real-time data, detecting inefficiencies instantly. This proactive approach can reduce energy waste significantly.
Another promising technology is the use of advanced materials. Nanocrystalline cores offer lower losses compared to traditional materials. These new materials can improve energy retention and reliability. Yet, they are not widely adopted due to high initial costs. This raises questions about their long-term viability.
Digital twins are also gaining traction. They create virtual models of transformers, allowing predictive maintenance. This can save costs and avoid unexpected failures. However, the integration of such systems requires significant investment. Many companies are still hesitant, weighing the potential versus the risks. Transforming legacy systems into smart grids seems a monumental task. The path forward remains unclear, but the push for better efficiency continues.
The energy efficiency of transformers is critical for sustainable electricity distribution. In 2026, the gap between conventional and advanced transformers has become even more pronounced. Conventional transformers typically exhibit lower efficiency. Their design often leads to higher energy losses, especially under varying loads. This can translate to significant energy waste, raising operational costs for utilities.
On the other hand, advanced transformers utilize innovative materials and designs. These enhancements result in improved energy performance. For instance, new core materials reduce losses significantly. The cooling systems in advanced designs can also optimize performance under high loads. However, these technologies come with higher upfront costs. Not all utilities can afford to make the switch immediately.
Moreover, while advanced transformers offer better efficiency, practical issues can arise. Installation can be complex, requiring skilled labor. Maintenance practices may also need updates to fully leverage their capabilities. Utilities must weigh the long-term benefits against initial challenges and costs. Balancing these factors influences the pace of adopting advanced technologies in the industry.
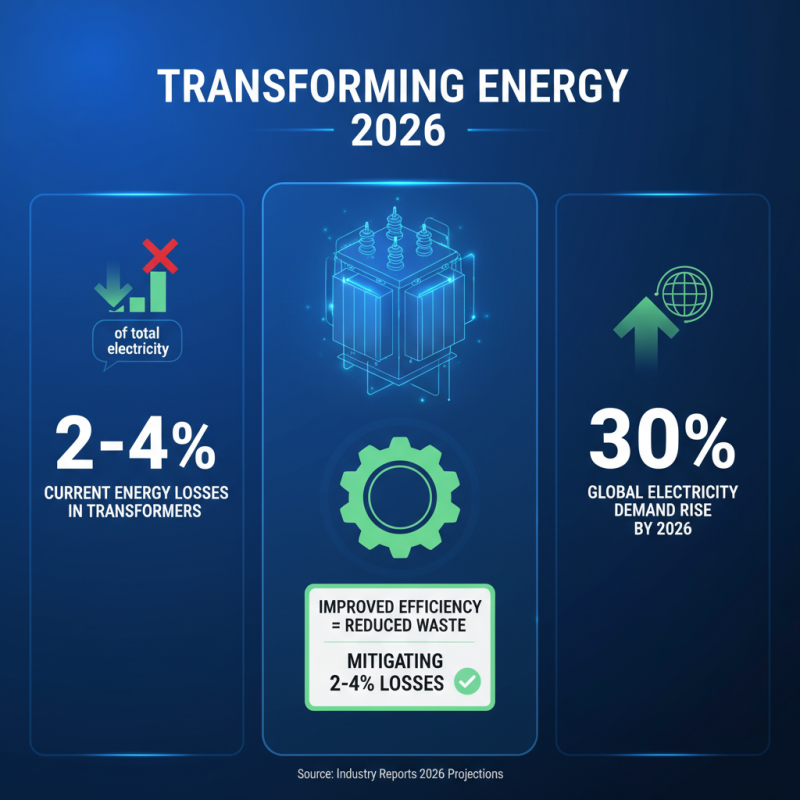
As we look towards 2026, energy efficiency in transformers is set to evolve significantly. Industry reports indicate that energy losses in transformers account for about 2-4% of total electricity. This is a significant figure, especially considering the global electricity demand is expected to rise by 30% by 2026. Improving transformer efficiency could help mitigate these losses, which would otherwise contribute heavily to energy waste.
Innovations in materials are expected to play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency. Advanced core materials, such as amorphous steel, have shown potential for reducing energy losses. A recent study suggests that switching to these materials can improve transformer efficiency by up to 15%. However, the implementation of such technologies is often slow and can face resistance due to cost implications. The industry must balance the initial investment with long-term savings and environmental benefits.
Additionally, regulatory changes will likely shape efficiency standards. The International Electrotechnical Commission is under pressure to tighten regulations on transformer efficiency. Their guidelines could dramatically influence manufacturing practices. However, not all manufacturers are prepared for immediate compliance. There is a sense of urgency, yet challenges remain in adapting to new standards while maintaining production costs. The path to enhanced energy efficiency in transformers is promising but fraught with hurdles.